Introduction and Analysis of Plane Trusses
Structure and Structural forms
Conditions of equilibrium
Load Transfer Mechanism in a Structural system
Degree of freedom,
Static and kinematic indeterminacies of structural systems
Difference Between Determinate and Indeterminate Structures
Types of trusses, Assumptions in analysis
Analysis of determinate trusses by method of joints and method of sections.
Deflection of Beams
Definition of slope,
Deflection and curvature,
Sign conventions,
Derivation of moment-curvature equation.
Double integration method and Macaulay’s method:
Slope and deflection for standard loading cases and for determinate prismatic beams subjected to point loads,
UDL, UVL and couple.
Moment area method:
Introduction
1st Mohr’s theorem,
2nd Mohsr’s theorems
Sign conventions,
Cantilever beam subjected to point load at free end
Cantilever beam subjected to udl throughout entire span
Conjugate beam method:
Real beam and conjugate beam,
conjugate beam theorems,
Application of conjugate beam method of determinate beams of variable cross sections.
Energy Principles and Energy Theorems
Principle of virtual displacements,
Principle of virtual forces,
Strain energy and complimentary energy,
Strain energy due to axial force,
bending, shear and torsion,
Deflection of determinate beams and trusses using total strain energy,
Deflection at the point of application of single load,
Castigliano’s theorems and its application to estimate the deflections of trusses,
bent frames,
Special applications-Dummy unit load method.
Arches and Cable Structures
Introduction and types of arches
Components of Arch
Analysis of Arches
Three hinged parabolic arches with supports different levels.
Determination of normal thrust and radial shear
cables - Introduction and types of cables
Analysis of cables under point loads .
Analysis of cables under point UDL.
Length of cables subjected to udl
Length of cables for supports at same and at different levels- Stiffening trusses for suspension cables.
Influence Lines and Moving Loads
Concepts of influence lines-ILD for reactions,
SF and BM for determinate beams-ILD for axial forces in determinate trussesReactions,
BM and SF in determinate beams using rolling loads concepts.
Structure and Structural forms
Conditions of equilibrium
Load Transfer Mechanism in a Structural system
Degree of freedom,
Static and kinematic indeterminacies of structural systems
Difference Between Determinate and Indeterminate Structures
Types of trusses, Assumptions in analysis
Analysis of determinate trusses by method of joints and method of sections.
Deflection of Beams
Definition of slope,
Deflection and curvature,
Sign conventions,
Derivation of moment-curvature equation.
Double integration method and Macaulay’s method:
Slope and deflection for standard loading cases and for determinate prismatic beams subjected to point loads,
UDL, UVL and couple.
Moment area method:
Introduction
1st Mohr’s theorem,
2nd Mohsr’s theorems
Sign conventions,
Cantilever beam subjected to point load at free end
Cantilever beam subjected to udl throughout entire span
Conjugate beam method:
Real beam and conjugate beam,
conjugate beam theorems,
Application of conjugate beam method of determinate beams of variable cross sections.
Energy Principles and Energy Theorems
Principle of virtual displacements,
Principle of virtual forces,
Strain energy and complimentary energy,
Strain energy due to axial force,
bending, shear and torsion,
Deflection of determinate beams and trusses using total strain energy,
Deflection at the point of application of single load,
Castigliano’s theorems and its application to estimate the deflections of trusses,
bent frames,
Special applications-Dummy unit load method.
Arches and Cable Structures
Introduction and types of arches
Components of Arch
Analysis of Arches
Three hinged parabolic arches with supports different levels.
Determination of normal thrust and radial shear
cables - Introduction and types of cables
Analysis of cables under point loads .
Analysis of cables under point UDL.
Length of cables subjected to udl
Length of cables for supports at same and at different levels- Stiffening trusses for suspension cables.
Influence Lines and Moving Loads
Concepts of influence lines-ILD for reactions,
SF and BM for determinate beams-ILD for axial forces in determinate trussesReactions,
BM and SF in determinate beams using rolling loads concepts.
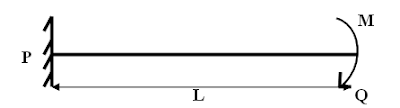
Please explain about Continues beems in briefly
ReplyDeleteEnter your comment...Really helpful, thanks alot
ReplyDeleteRC Assignment 3rd year Civil enginering
ReplyDeleteP.107--------------------Assignment-2
1.Floor systems are sustained by parallel T-beam of span 6m and 1.8m on center to center spacing.the total design moment is 450KNm.
Dimensions for the beam D=400mm,bw=300mm flange depth,hf=80mm….
material used are fcu=25MPa,fyk=300MPa and class 1 works.Design interior beam.
2.Design the edge beam using 2/3 of the bending moment and with the same data in…Eg.1.
3.Design a T-beam with be=1000mm,hf=100mm,bw=250mm,d=450mm,use c-25 concrete and s-460 steel,class 1 works;M=470KNm
5.A T-bea has are effective flange width of 760mm,bw=350mm,hf=100mm and effective depth,d=500mm if s-400 steel,fyk=20MPa,class 2 works are used.what will be the design moment capacity for this beam when As=900mm^2 is used?
P.77-----------------Assignment-1
6.the longitudinal reinforcement bars for abeam is indicated in the figure below.determine the maximum moments using c-20,s-360 and class 2 work.
Length..400mm,width…300mm,5∅20…OOOOO
8.A cantilever beam 4m span carries alive load of 150KN/m in addition to its own weight.
A)Design the beam section for Ultimate limit state for flexural using uniform depth
B)Redesign the same beam for ultimate limit state for flexural using linearly varying depth(depth at free end is 1/3 of at fixed end). ω
Use=C-30MPa(fcd=13.4MPa)
S-300MPa(fyd=260.87MPa)
( Up sign) ∝RC=24KN/m^3
Design constants using ρmax=0.75ρb are ωmax=0.437 and μmax=0.34
4.A simply supported beam spans 8m and is subjected to a live load of 30KN/m in addition to self weight.materials used are c-25,s-300 and class 2 work.if width L=250mm,determine the depth required to satisfy section at mild-span and the corresponding flexural reinforcement.
Finaly sketch it available bars are ∅16mm and ∅10mm.
Address….Email:-asegidt504@gmail.com
Hello everyone.
ReplyDeleteI am facing problem in etab. My etab analysis is showing negative axial load (DL+LL) at some joints. Please help me out of this. What might be the reasons behind it.