Definitions
Load: Load
is a criterion which gives a clear picture about the strength of a material. It
is an external pressure or impact offered against the inter molecular bond of
the object which results in deformation (or fracture) of the object.
Stress: The intensity of the resisting force offered by the
inter molecular bonding of the object per unit area towards the load applied
before the failure of the object is called as stress.
Generally stress is represented
as c or f
Hence σ = P /A
or W /A (Since P=W)
Where
P= load applied, W= bond resisting
force
, A = area of cross section of the material.
SI
units of stress are N/mm2, N/m2, N /cm2
Note:
|
CONVERSIONS
|
|
|
1kg
|
10N
|
|
1m
|
1000mm
|
|
1m
|
100cm
|
|
1cm
|
10mm
|
|
1mm
|
0.1cm
|
|
1mm
|
0.001m
|
|
1cm
|
0.01m
|
|
1pa
|
1N/m2
|
|
1GN
|
109N
|
|
1MN
|
106N
|
|
1GN
|
103N
|
|
1N/mm2
|
106N/m2
|
Strain: When the object is subjected to the external force,
initially at the equilibrium condition (P=W) the deformation effect is negligible.
But with the gradual increase in the magnitude of the applied load, the
dimensions of the object will be altered due to the deformation effect.
Therefore the ratio of change in the dimension (due to deformation effect) of
the object to its original dimension (at equilibrium condition) is termed as
strain of the object.
Strain is a unit less quantity.
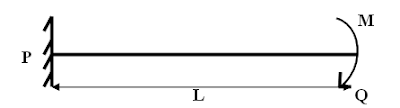
TYPES OF STRESS AND STRAIN : Tensile
stress and tensile strain
Consider a uniform bar of cross sectional area A subjected to an axial tensile force P. The stress at any section x-x normal to the line of action of the tensile force P is specifically called tensile stress. Since internal resistance R at x-x is equal to the applied force P, we have,
Tensile stress = (internal resistance at x-x)/(resisting area at x-x)
= R/A
= P/A.
Where,
P=Tensile load
L =Original length
dl=Elongation
L+ dl=Increase in length with respect to original length
Under tensile stress the bar suffers stretching
or elongation.Therefore ratio of increase in length to the original length is
termed as tensile strain.
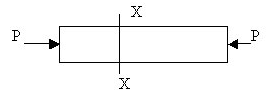
Compressive stress and strain
If the bar is subjected to axial compression instead of axial tension, the stress developed at x-x is specifically called compressive stress.
Compressive stress = (internal resistance at x-x)/(resisting area at x-x)
If the bar is subjected to axial compression instead of axial tension, the stress developed at x-x is specifically called compressive stress.
Compressive stress = (internal resistance at x-x)/(resisting area at x-x)
= R/A
= P/A.
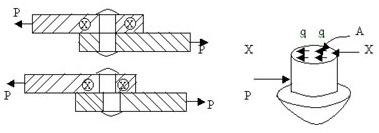
Shear Stress
The stresses set up at
the section x-x acts along the surface of the section, that is, along a
direction tangential to the section. It is specifically called shear or
tangential stress at the section and is denoted by q.
q = R/A
= P/A.
q = R/A
= P/A.
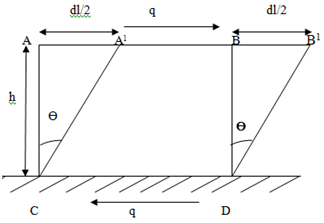
Where,
Shear strain ϴ =Transverse
displacement/Distance AC= (dl/2)/h
Tan ϴ= ϴ (since it is small)




Your website is very beautiful or Articles. I love it thank you for sharing for everyone. Civil Engineering online courses
ReplyDeleteVery significant Information for us, I have think the representation of this Information is actually superb one. This is my first visit to your site. Autoindustri
ReplyDeleteIt is a very informative and useful post thanks it is good material to read this post increases my knowledge. engenharia de produção
ReplyDeleteEnzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction by the active site of a protein. In principle, the mechanism of enzyme catalysis is similar to other types of chemical catalysis. bond strain
ReplyDeleteI just want to thank you for sharing your information and your site or blog this is simple but nice Information I’ve ever seen i like it i learn something today. Cbd pet health sprays
ReplyDeleteWow what a great blog, i really enjoyed reading this, good luck in your work. Russia medical college
ReplyDelete